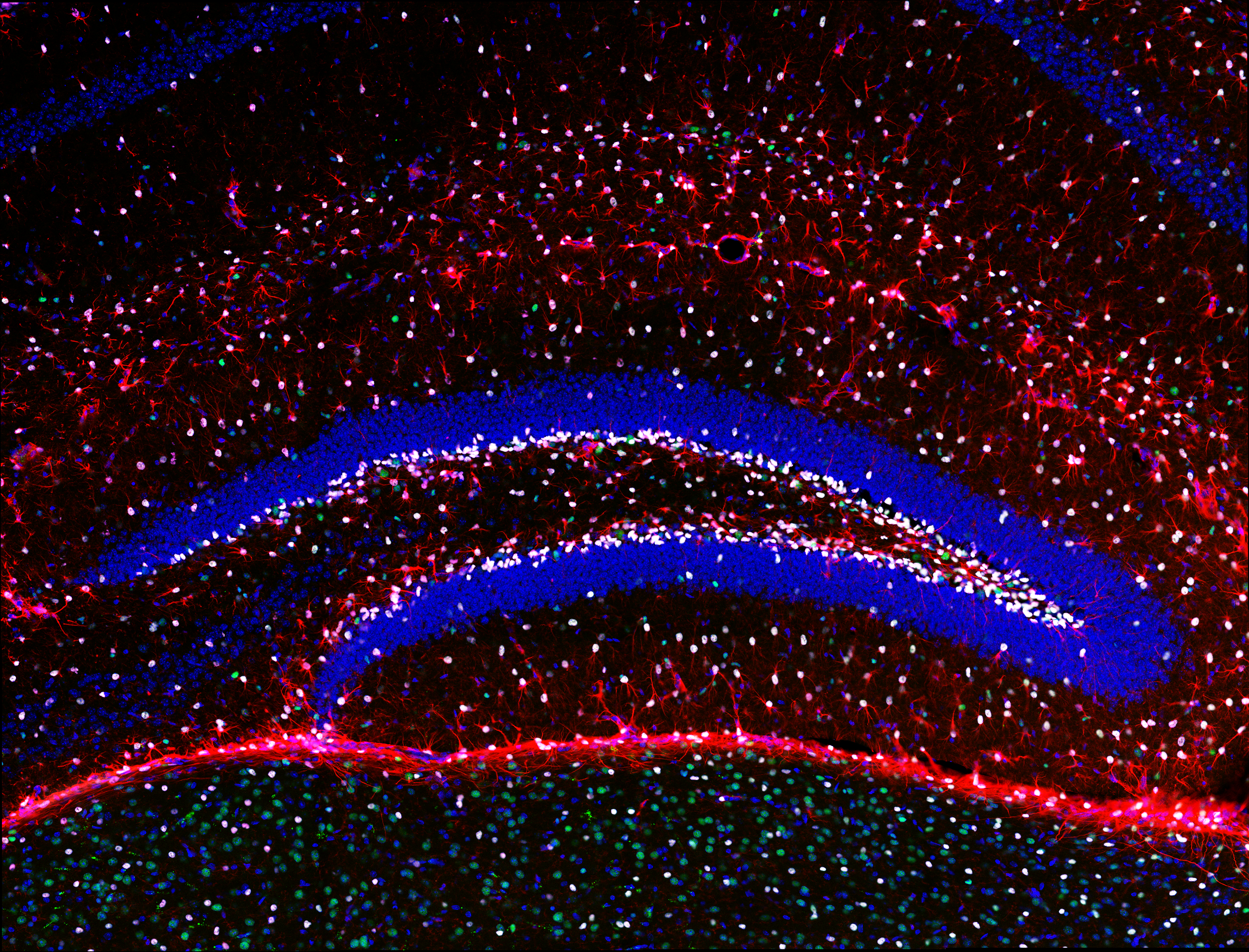
Fezf2 promotes differentiation in hippocampal post-natal neural stem cells
Physical and Biological Sciences
BIOL 195
The vast majority of neurons are generated before birth. However, there are two distinct stem cell niches that generate neurons postnatally, the Subgranular Zone (SGZ) of the hippocampus and Subventricular Zone. The balance of new neuron production and stem cell depletion in adult neural stem cells is tightly regulated by transcription factors. One transcription factor, Fezf2, has been extensively studied in the cortex during embryonic stages. However, its expression in the post-natal stem cell niches has not been previously reported and its function is unknown. We found that Fezf2 is specifically expressed in the majority of Sox2+ GFAP+ post-natal neural stem cells. To understand the function of Fezf2 in postnatal neural stem cells, we analyzed the Fezf2 mutant phenotype in the hippocampus and performed CUT&RUN to identify potential binding targets. We found that Fezf2 induces differentiation by potentially inhibiting the Notch pathway.